India has emerged as a rare bright spot in the global economy, with its gross domestic product (GDP) expanding by a robust 8.4% in the final quarter of 2023 amid slowing growth worldwide as stated in the Quarterly Estimates of Gross Domestic Product for the Third Quarter (October-December), 2023-24.
The country’s strong performance defied expectations and highlighted its economic resilience, positioning India as the world’s fastest-growing major economy.
Highlights of India’s Economic Report Card
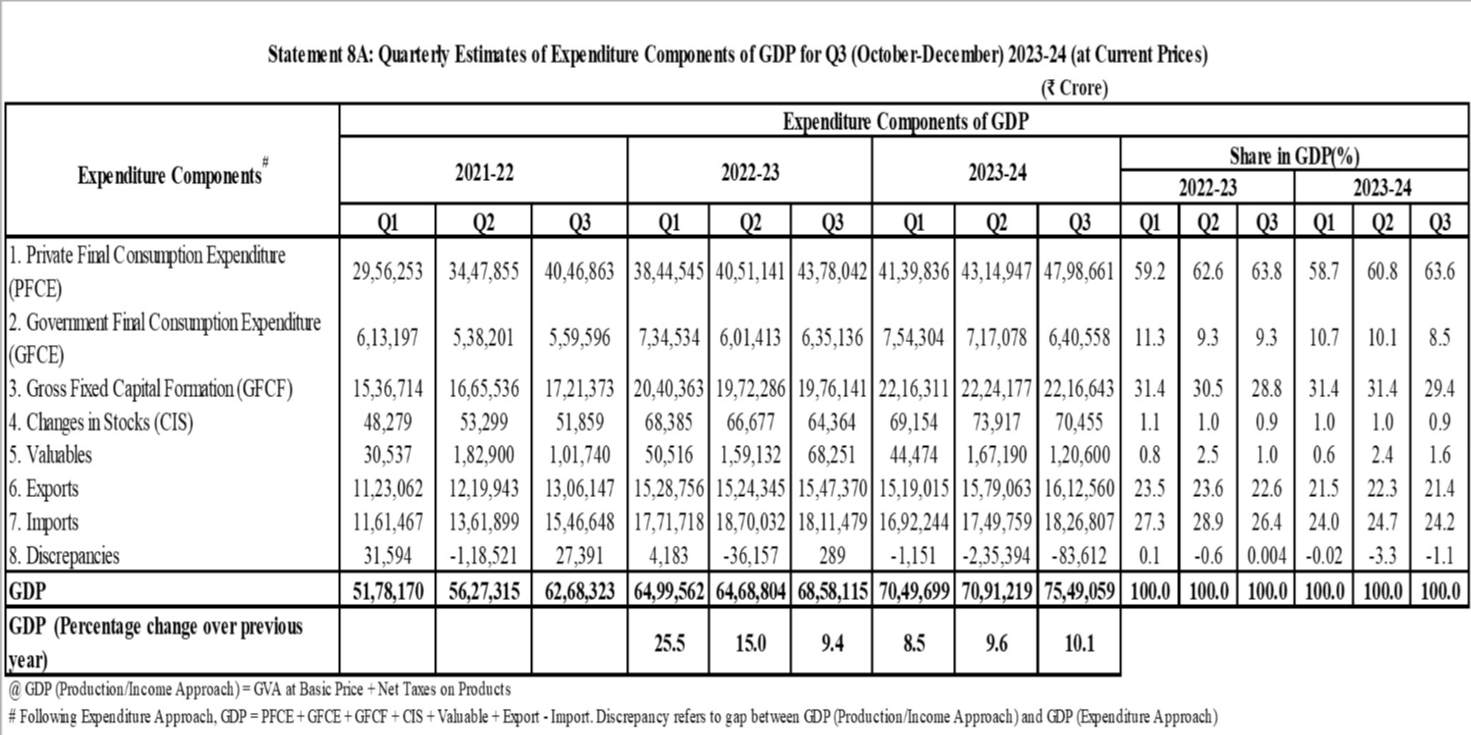
- The country’s GDP growth in October-December 2023 hit 8.4%, driven by double-digit expansion in manufacturing and solid growth in sectors like construction.
- The annual GDP growth estimate for 2023-24 has been pegged at a remarkable 7.6% by government data, exceeding the RBI’s projection.
- In comparison, China reported economic growth of just 3% in 2022 while the global economy is expected to expand by just 2.9% in 2023 according to IMF.
- The country’s growth trajectory reinforces projections of it becoming the world’s third-largest economy by 2027.
What Propelled Robust Growth?
Several factors powered India’s economic surge in late 2023:
- Manufacturing rebound: The manufacturing sector saw 11.6% growth in Q3 FY 2024, recovering strongly from pandemic downturns.
- Infrastructure push: Government programs like PM GatiShakti catalyzed 9.5% growth in construction – a crucial job creator.
- Festive boost: Pent-up demand during the festive season fueled spending and supported the growth uptick.
- Investor interest: The country attracted over $70 billion in funding in 2023 as investor confidence grew.
- Services rebound: With COVID-19 impacts waning, trade, hotels, transport and communications bounced back.
India Outperforms Major Economies
- Compared to major world economies grappling with inflation or recession, India’s growth momentum stood out in 2023.
- Advanced economies like the US grew by just 2.1% amidst high energy costs and interest rate hikes.
- China reported 2.7% full-year growth in 2022 – its second lowest rate in 40 years due to COVID curbs and real estate crisis.
India’s Growth Trajectory Lauded
India’s strong economic report card has earned praise from organizations like the IMF:
- IMF Chief Economist Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas described India as a “bright spot” in the global economy.
- An IMF report forecast 6.1% growth for India in 2023 while the world economy decelerates sharply.
“As the world suffers the economic costs of war, supply chain disruptions and health crises, India’s economy remains a rare bastion of growth” Gourinchas added.
Government Efforts to Deepen Growth
Experts have credited structural reforms and government policies for sustaining domestic demand momentum.
Key policy measures that shored up growth include:
1. Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Provided over $30 billion in incentives across 14 key sectors like electronics and solar PV manufacturing.
2. National Infrastructure Pipeline: Announced $1.5 trillion investment in infrastructure like energy, transport, IT over 5 years.
3. National Monetization Pipeline: Plans monetization of brownfield infrastructure assets across roads and railways.
4. FDI Liberalization: Policy changes opened up new sectors like insurance, infrastructure and startups to greater foreign investment.
Growth Supports India’s Rise in Global Economy
With growth beating expectations, India is poised to climb the ranks of the world’s largest economies.
- India recently surpassed the UK to become the 5th largest economy.
- By 2027, India could surpass Japan and Germany to emerge as the 3rd biggest global economic powerhouse.
The country’s expanding footprint as a investment and manufacturing destination will support its global ascent.
With sound economic fundamentals, analysts see India’s growth story gaining momentum as the world contends with a tough year ahead.
Financial Inclusion Initiatives Expand Access
Alongside GDP growth, India has undertaken game changing financial inclusion programs to empower rural citizens and drive equitable progress.
Key government-led initiatives include:
Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) Trinity
This flagship program aims to link bank accounts, mobile numbers and Aadhaar cards of Indians to plug leakages and enhance transparency.
Impact: Enabled DBT transfer of $1.5 trillion in subsidies during past 7 years.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- Launched in 2014, PMJDY focused on increasing banking access for unbanked and underserved households.
- It facilitated opening of 470 million bank accounts so far through Business Correspondent outlets.
Stand Up India Scheme
The program aims to support SC/ST and women entrepreneurs through collateral-free loans up to ₹10 lakh.
Impact: Empowered over 250,000 new entrepreneurs across sectors like textiles, agriculture and services.
Digital Shift Expanding Financial Inclusion
India’s JAM trinity and technological innovations have been pivotal in bridging economic divides.
- RuPay: Domestic card network RuPay grew to achieve near universal coverage, registering 3 billion transactions worth ₹6 trillion in FY 2022-23.
- UPI Transactions: Unified Payments Interface (UPI) reported 81 billion real time transactions in 2023, reflecting digital adoption.
- Open Banking: Account aggregator system links bank accounts with financial information providers upon user consent – securely enabling wider credit access4.
The financial inclusion landscape has undergone a tectonic shift – with Jan Dhan accounts, low KYC wallets and UPI fast replacing cash. More remains to be done but the roadmap is promising.
Also Read: Central Bank Amends Regulatory Reporting Protocols for Banks & NBFCs












Comments 2