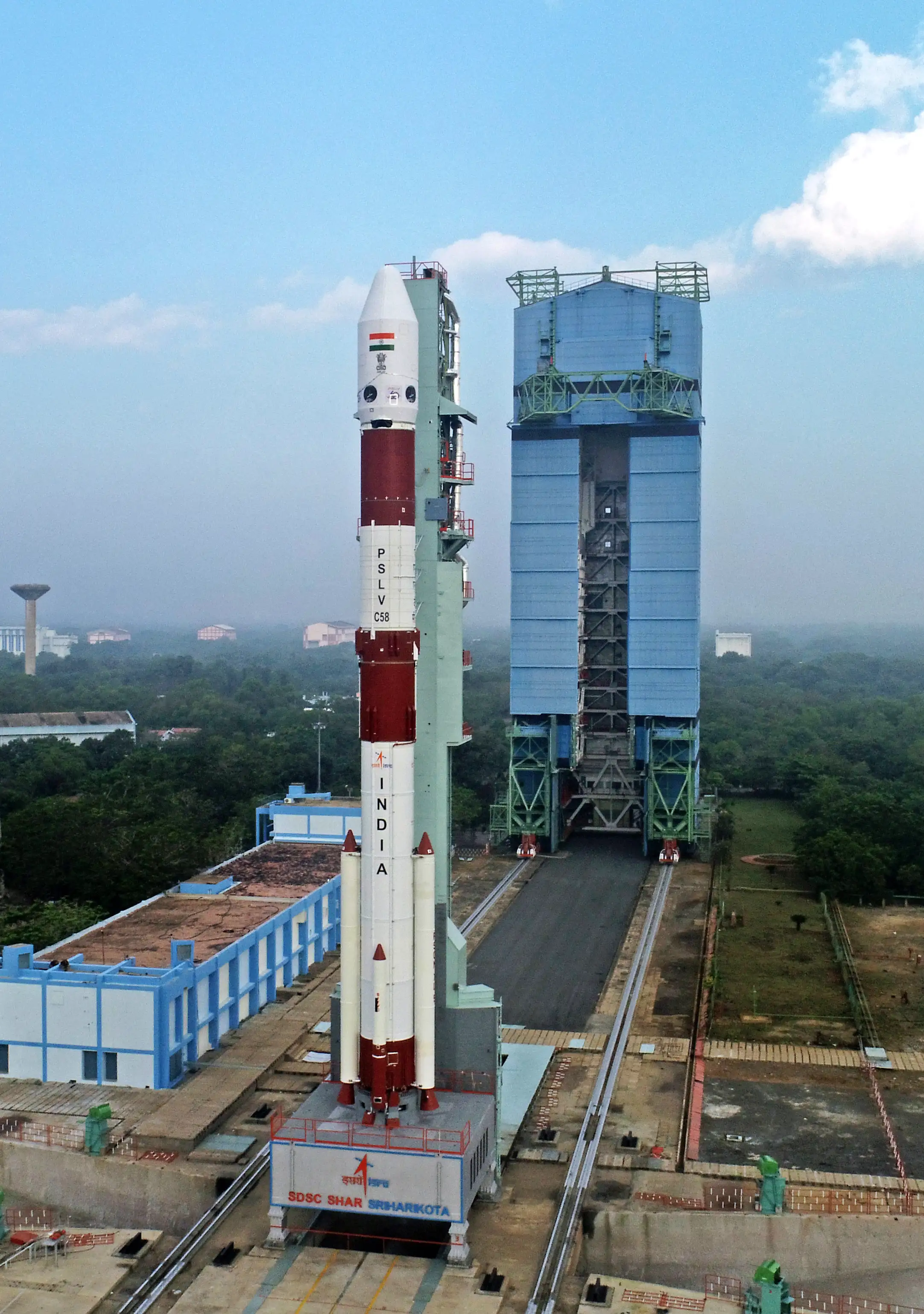
In a stellar start to the new year, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) embarked on its maiden space mission of 2024. Monday, January 1st, saw the successful launch of the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat). The satellite gracefully ascended into the skies at 9:10 AM, lifting off from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
Following the Chandrayaan-3 and Aditya L1 mission’s trail, the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) launch marks yet another pivotal stride in India’s celestial journey.

The ‘PSLV Orbital Experimental Module,’ abbreviated as POEM, is set to play a pivotal role as the fourth stage of the upcoming 60th Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) flight. Its primary mission is to carry the XPoSAT, or X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, as the focal payload. This marks another significant stride in India’s space exploration endeavours.
This pioneering satellite is set to propel India into an elite league, making it the second nation globally—after the United States—to dispatch a dedicated astronomy observatory. XPoSat is geared towards unravelling the mysteries of black holes and neutron stars that inhabit our galaxy.
What is XPoSat?
XPoSat, the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, represents a historic milestone as the premier dedicated scientific satellite from ISRO designed specifically for researching space-based polarisation measurements of X-ray emissions from celestial sources. The satellite’s configuration modifies the IMS-2 bus platform, drawing on the heritage of IRS satellites for its mainframe systems.
The technological prowess of XPoSat is exemplified by its two payloads: POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) and XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing). The development of POLIX is credited to the Raman Research Institute. At the same time, the Space Astronomy Group of URSC has played a pivotal role in bringing XSPECT to fruition.
What are the objectives of the mission?

The mission has a clear set of objectives:
- Utilising the POLIX payload, measure the polarisation of X-rays within the energy range of 8-30 keV originating from approximately 50 potential cosmic sources, employing Thomson Scattering as the methodology.
- Leverage the XSPECT payload to conduct extensive and prolonged spectral and temporal studies of cosmic X-ray sources, focusing on the 0.8-15 keV energy band.
- Simultaneously, perform polarisation and spectroscopic measurements of X-ray emissions from cosmic sources using the POLIX and XSPECT payloads within a shared energy band. This multifaceted approach aims to deepen our understanding of celestial phenomena across various dimensions.
What are the scientific goals of the mission?
The mission’s scientific goals are ambitious and comprehensive:
- Investigate the distribution of magnetic fields, geometric anisotropies, alignment concerning the line of sight, and the nature of accelerators in galactic cosmic X-ray sources. This involves measuring the degree of polarisation and its angle.
- Examine the structure and geometry of the magnetic fields surrounding neutron stars, decipher the mechanism of X-ray beaming, and explore its correlation with luminosity and the mass of accretion rate in powered pulsars.
- Attain a detailed understanding of galactic black hole binary sources, shedding light on their intricate characteristics.
- Delve into the study and confirmation of X-ray production, discerning whether it originates from the polar cap of a neutron star or the outer cap of a pulsar magnetosphere.
- Differentiate and confirm the dominance of the synchrotron mechanism over thermal emission in Supernova remnants, providing valuable insights into the underlying processes of X-ray production in these cosmic phenomena.
What are the experiments to be performed by POEM?

The experiments lined up for POEM are diverse and impressive:
- Bellatrix Aerospace (Bengaluru):
-
- Rudra 0.3 HPGP: A green monopropellant thruster.
- ARKA-200: A heater-less hollow cathode for Hall thrusters.
- InspeCity Space Labs (Mumbai):
-
- Green Impulse TrAnsmitter (GITA): A green bipropellant CubeSat propulsion unit.
- TakeMe2Space (Hyderabad):
-
- Radiation Shielding Experimental Module (RSEM): Designed to assess the effectiveness of Tantalum coating, enhancing CubeSat lifespan.
- LBS Institute of Technology for Women (Thiruvananthapuram):
-
- Women Engineered Satellite (WESAT): Measuring solar irradiance and UV Index.
- Women Engineered Satellite (WESAT): Measuring solar irradiance and UV Index.
- KJ Somaiya Institute of Technology (Mumbai):
-
- BeliefSat-0: An amateur radio satellite.
- ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC):
-
- Fuel Cell Power System (FCPS)
- Silicon-based High Energy Cell
- Physical Research Laboratory (Ahmedabad):
-
- Dust Experiment (DEX): Designed to measure interplanetary dust count.











