EY’s recent report, “AIdea of India: Generative AI’s Potential to Accelerate India’s Digital Transformation,” highlights the significant economic impact of Generative AI (GenAI) on India. The findings suggest that GenAI could contribute a substantial $1.2 – 1.5 trillion to India’s GDP over the next seven years. In the specific timeframe of 2029-30, the report indicates that GenAI has the potential to further boost India’s GDP by an impressive $359-438 billion alone.

GenAI’s Rapid Impact on India’s GDP
The rapid global growth of Generative AI (GenAI), attributed to its ability to enhance enterprise productivity and efficiency, holds the potential to propel India’s economic expansion significantly.
The EY report emphasises the rising adoption of GenAI and provides valuable insights into how Indian enterprises can optimise their benefits.
Against the backdrop of global institutions like the World Bank and the IMF, which recognise India as one of the fastest-growing economies, the study underscores the prospect of a substantial GDP boost for the nation.
EY’s predictions indicate that within just seven years, the cumulative impact of GenAI could range from US$1.2 trillion to US$1.5 trillion, contributing an additional 0.9% to 1.1% in the annual Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
According to the EY report, a substantial 69 per cent of the anticipated impact of Generative AI (GenAI) on India’s GDP is projected to stem from various sectors. These include business services encompassing IT, legal, consulting, outsourcing, rental of machinery and equipment, as well as financial services, education, retail, and healthcare.
EY Advocates Proactive Regulatory Measures for GenAI
EY underscores India’s economic prowess, positioning it among the world’s fastest-growing despite global challenges. The nation’s trajectory toward becoming the third-largest economy by 2027 is intricately tied to the transformative influence of Generative AI (GenAI).

As the company report outlines, adopting GenAI is vital in adding a substantial US$359 billion to US$438 billion to India’s GDP in the fiscal year 2029-30 alone. Looking at the broader picture over seven years, from 2023-24 to 2029-30, this translates to an impressive additional contribution of 5.9% to 7.2% of the GDP.
EY highlights the necessity of a proactive regulatory approach to unlock the full potential of Generative AI (GenAI), emphasising the importance of ensuring citizen safety. The report suggests that the government can play a pivotal role by facilitating access to essential digital infrastructure. This includes initiatives such as the widespread deployment of 5G, developing robust data centres, ensuring access to specialised chips, and establishing dedicated AI computing infrastructure.
Moreover, the report recommends the implementation of policies geared towards nurturing and attracting specialised talent in the field of AI. By fostering an environment encouraging expertise and innovation, the government can contribute significantly to the responsible and effective integration of GenAI into the broader societal framework.
GenAI Adoption Challenges in India
The study underscores that a significant 75 per cent of businesses in India currently exhibit a low to moderate readiness to harness the benefits of Generative AI (GenAI).
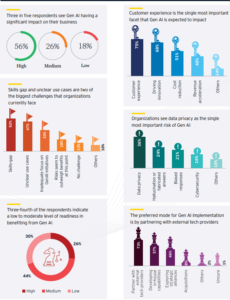
Within this landscape, the report reveals that 52 per cent of surveyed organisations identify a skills gap as a notable challenge in fully realising the potential of GenAI for their businesses. Additionally, approximately 42 per cent of respondents find the availability of unclear use cases to be another hurdle in adopting GenAI.
The report suggests strategic measures to foster GenAI innovation, including enabling access to training data and marketplaces, deploying GenAI systems as public goods, securing critical digital infrastructure, and facilitating access to talent through public funding of Research and Development.
Turning to data privacy, the report sheds light on organisational concerns, with 36 per cent highlighting data privacy as the single most critical risk associated with GenAI. Other perceived risks include the potential for hallucination or fabricated answers (24 per cent), biased responses (21 per cent), and cybersecurity threats (16 per cent). Addressing these concerns is crucial for building trust and ensuring the responsible implementation of GenAI technologies.
The study reveals that 75 per cent of organisations identify customer engagement as the segment most profoundly impacted by Generative AI (GenAI). Moreover, the report notes that 73% of organisations prefer collaborating with external tech providers when implementing GenAI.
Experts in the report emphasise that the extent of GenAI’s influence in each sector hinges on factors such as feasibility, adoption rates, and the respective contribution of each industry segment to India’s overall economic activity. This nuanced perspective underscores the need for tailored strategies to maximise the impact of GenAI across diverse sectors.












Comments 2